Medical Record Management
Challenges in Medical Record Management
- Unsolicited data
- Logistical Problems
- Physical Problems
- Ethical Problems
- Accessibility
- Storage
- Access
- Safety
- Security
- Inadequate funding as regards record management.
- Inadequate supply of computers and other ICT devices for record preservation.
- Inadequate skill in computer utilization.
- Outdated or non-existence of hardware, software, and network connectivity.
- Harsh environmental conditions accelerating record material depreciation.
- Lack of preservation and conservation policy.
- Inadequate infrastructure to enhance record management.
- Consumer expectations
- Compliance with records management procedure and tools in accordance with service delivery;
- Records Management Unit (RMU) assistance and location of patient files
- Location and length of time for retrieval of medical records
- Patient satisfaction with records management at the public hospital
- Impact of records management structure on service delivery
- Paper-based systems negatively impact patient records.
- Medical records are currently managed physically, which is drastically affecting compliance and causing revenue loss for the healthcare organization.
- Data is accessed by multiple devices which causes data breaches.
- Third-party use medical information to access medical products
- Safe data storage is a pressing need
Advantages/Benefits
- Free staff training
- No upfront cost
- Easy to use
- 24/7 support
- Stringent security
- Increased revenues
- Medical records management system in place that includes automating, capturing, storing, and disseminating records
- The system improves record location and tracking, even for records people don’t frequently use
- It can also preserve historical and vital information about a medical facility in case of a disaster or legal requirement
- A records management system can also make it easy to transfer or release information between offices
- Both patients and physicians can access the information in a timely manner without duplicating efforts
- This type of visibility can increase patient safety, reduce mistakes, and increase confidence in a treatment plan
- From a productivity standpoint, medical records management might address litigation risks, lower operating costs (due to reduced physical storage needs), and boost employee productivity, mobility, and efficiency
- Allowing connections between billing and other systems
- Increase in speed of information exchange
- Storage cost is much less than the equivalent number of paper records.
- Easy to copy and take very small amount of time.
- Hospital stays are reduced with more efficient processes and automatic routing of medical information.
- Fewer mistakes are made that could affect patient care since patient information.
How Does CRM Work?
Store Records Electronically
- Use templates to provide advisory faster than paper
Specialty Based Module:
- Use dental charts
- Vaccination plans
- Eye charts
- Other specialty-based modules
Electronic Invoicing:
- Generate invoices electronically
- Keep track of patient billing histories and pending payments.
Reports and Analytics:
- Extract reports on custom filters
- Use analytics to make informed decisions
Techniques/Methods Used for MRM
EMR (Electronic Medical Record)
- EMR systems are widely used in hospitals, nursing facilities, healthcare, clinics, laboratory facilities, treatment centers, and physician’s offices.
Medical and clinical data gathered in one provider’s office.
- Narrower view
- Digital version of a paper chart in one office
- Not designed for sharing
- Providers use mainly for diagnosis and treatment
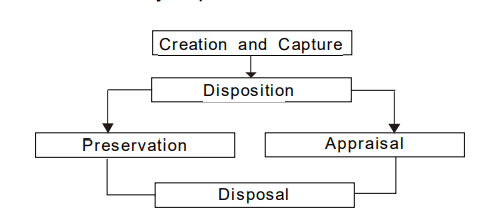
Lifecycle of Electronic Medical Records
- Create and capture refers to the initial creation or capture of a record within an established Records Management System
- Disposition refers to the initial decisions that are made on the estimated retention period for a record when it is no longer active
- Appraisal refers to the decision-making process based on a set of guidelines to determine whether the record is kept in the permanent preservation or destroyed.
- Preservation refers to the strategies and methods of migrating and keeping the records for future access by upgrading to the latest hardware and software platforms.
- Disposal refers to the process of transferring the records to permanent archives, preservation or for final destruction.
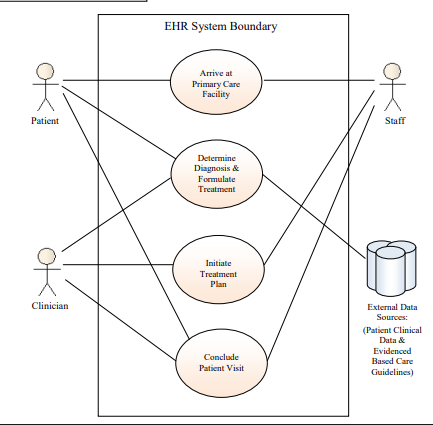
Patient Presents
- The clinician and staff must assess current state and confirm eligibility of patient
- Enter current vital information into the EHR
- Electronically conduct real-time (i.e., at the point of care) eligibility, benefits checking, and prior-authorization activities
Determine Diagnosis
- Integrate clinical data from multiple sources to form a comprehensive view of the patient’s supporting data and history.
- May require the option to distinguish information received from various sources: clinician’s EHR, other facilities, patient’s PHR, pharmacist, etc.
- Incorporate applicable standards of care, care plans, and evidence-based guidelines.
- Incorporate eligibility and coverage information into decision criteria.
- May require ability to consult outside clinical resources to inform diagnosis and treatment
EHR (Electronic Health Record)
- EHR technology to engage patients and families, improve safety, efficiency, and quality, reduce health disparities, improve care coordination and overall population and public health, and maintain privacy and security of patient health information.
Medical and clinical data gathered from many providers’ offices and hospitals
- Broader View
- Digital version of varied health information
- Designed for sharing outside of an individual medical practice
- Providers have access to many diagnostic tools to make decisions
Initiate a Treatment Plan
- Order procedures via a computerized physician order entry
- Prescribe medications via electronic prescribing.
- Enter staff instruction in EHR.
- Coordinate treatment over time.
- Coordinate across multiple providers and transfer patient information
Conclude Patient Visit
- Document remaining visit information in EHR.
- Describe instructions to the patient regarding their course of treatment
- Schedule patient follow up procedures and visits as necessary.
PHR (Personal Health Record)
Personal health records are so important – it’s ownership over your own health care.
- A PHR is a personal health record, which individuals can use to track their own health information.
- Current medications and pharmacy information
- Immunizations
- Allergies
- Health history (including past procedures, surgeries, illnesses, and family history)
- Test and lab results
- Insurance paperwork
- Bills and receipts
Solutions
1. HRIM
Health Records Information Management (HRIM) increases productivity and cuts costs by giving healthcare professionals the information management tools they need to help them provide optimal care and improve patient outcomes
Capture Data
- Capture documents at any time using scanners, video, fax, mobile, email from your content management system
Integrate Information
- Integrate information from new documents as well as from backfile conversions to be consolidated and route it to electronic health records.
Accessibility
- Provide immediate accessibility by capturing all data deemed relevant by you from any hospital department or process on a single platform.
Improve quality
- Improve care quality by providing doctors, nurses, and clinicians with real-time access to patient data records, whether on-site or at remote locations
Processing
- Trace and audit the processing of all documents from the point of origination through archiving.
2. Smartsheet
Smartsheet, a work management and automation platform that enables enterprises and teams to work better
Centralized Information
- Create a centralized information hub in Smartsheet to store, track, and manage all patient documentation
Self Service Reports
- Provide real-time visibility into resources, status, and performance
Dashboard
- Rapidly align operations to strategy.
3. Shoreline:
Medical Records Management can be a significant challenge, Shoreline provide services to address all aspects of the document lifecycle.
Medical Record Storage
- We offer secure medical document storage in our records management facility
- We can efficiently store and track patient charts in hard copy format using our advanced barcode technology and enable fast retrieval in the event that a chart is needed.
Medical Record Scanning
- Shoreline provides outsourced patient chart scanning to enable you to retrieve medical records directly from your desktop or EMR system
- Scan on Demand Services to deliver back paper-based charts in imaged format.